Blog Archives
My new Miss. Baptist history book is now available!

My new book, Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, has been published by the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board, and is now available to the public. It is a hardback book, 300 pages of text, plus four appendices, notes, and an index in the back.
In 2021, I signed a contract with the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board and Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission to revise and update R.A. McLemore’s book published in 1971, A History of Mississippi Baptists. While the new work is based on McLemore’s history, it has many more new features than simply the addition of a half century of recent history. I have included new research from the beginning. For example, I discovered evidence that the mother church of Mississippi Baptists was Ebenezer Baptist Church, Florence, South Carolina. Other new research includes the declaration of religious liberty by Richard Curtis, Jr., the first Baptist pastor in Mississippi; social and cultural information on typical Baptist life during different time periods; trends in Baptist theology; and details of the previously untold story of the McCall controversy of 1948-49. Throughout the book, I sought to write in a narrative style, including anecdotes that reflected the flavor of Baptist life.
You can get a book by making a donation to the Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission at the link below. Click on “Donate to the Historical Commission,” then fill out the form, select “MS Baptist Historical Commission” and how much you will donate (I suggest at least $15 to cover their costs), and how many copies of the book you want.
Here is the link: https://mbcb.org/historicalcommission/
The chaotic 1930 special session of the Miss. Baptist Convention

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
On July 15, 1930, an unprecedented second special session of the Mississippi Baptist Convention met in Newton, attended by 318 messengers. It turned into chaos.
(A first special session had been held in April to respond to the problems of the Great Depression by closing Clarke College and moving the Mississippi Baptist Orphanage to the campus of Clarke; however, some legal matters were not handled, so a second special session was called.)
This second special session erupted into a chaotic state of confusion, described by The Baptist Record as featuring “unanimous disagreement, often vociferously expressed.” MBCB executive R.B. Gunter made a plea for harmony, but it went unheard. W.N. Taylor of Clinton presented resolutions to continue Clarke College and keep the orphanage near Jackson, in effect to rescind the vote of the previous session. Convention president Gates ruled the resolutions out of order, but a challenge was made to his ruling; the messengers voted 164-154 to sustain his ruling. Next, M.P. Love of Hattiesburg moved that the property of the orphanage be mortgaged to pay the debts of Clarke College, but his resolutions were voted down. At a stalemate, the messengers then adjourned to dinner.
The Baptist Record commented that the only thing the messengers agreed about was that “the people of Newton and vicinity furnished a good dinner.” After dinner, the messengers returned and reversed their earlier actions. This time, Gates’ ruling was overturned. Next, the messengers adopted Taylor’s resolutions, voting to keep the orphanage in Jackson and to re-open Clarke College. To pay for it, the messengers authorized the trustees to borrow the money, using the property of the college and orphanage as security. In addition, they pledged an extra $10,000 each to Blue Mountain College and Mississippi Woman’s College. The debacle of these two special sessions taught Mississippi Baptists a lesson they had not learned from the 1892 convention (which attempted to relocate Mississippi College, only to have it overturned later): attempts to operate their institutions from the floor of the convention could lead to great confusion and chaos.
(Dr. Rogers is the author of the new book, Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State.)
Mississippi Baptists and the civil rights struggle in the 1950s and 1960s
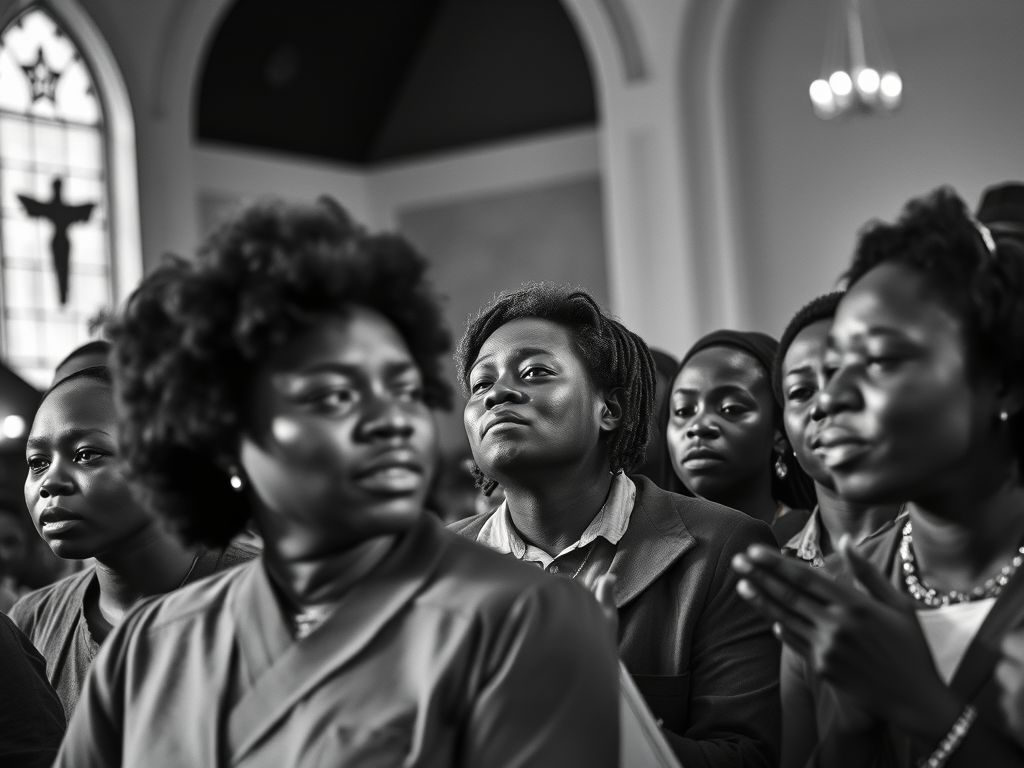
Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
On May 17, 1954, the Supreme Court struck down public school segregation in Brown v. Board of Education, saying, “Separate educational facilities are inherently unequal.” The Southern Baptist Convention, meeting only weeks later, became the first major religious denomination to endorse the decision, saying, “This Supreme Court decision is in harmony with the constitutional guarantee of equal freedom to all citizens, and with the Christian principles of equal justice and love for all men.” Mississippi Baptists, however, would have none of it. A.L. Goodrich, editor of The Baptist Record, accused the Southern Baptist Convention of inconsistency on the issue for not endorsing other types of integration as well. Goodrich was “indignant” at this example of “the church putting its finger in state matters,” but he told Mississippi Baptist readers that they “need not fear any results from this action.” First Baptist Church, Grenada (Grenada) made a statement condemning the Supreme Court decision. The Mississippi Baptist Convention, meeting November 16-18, 1954, passed several resolutions, but it made no mention of the Supreme Court decision.1
The Supreme Court deferred application of integration, and Mississippi’s governor, Hugh White, met with Black leaders, expecting that they would agree to maintain segregated schools if the state improved funding for Black schools. H.H. Humes represented the largest Black denomination in the state, as president of the 400,000-member General Missionary Baptist Convention. He responded to the governor, “the real trouble is that for too long you have given us schools in which we could study the earth through the floor and the stars through the roof.”2
In the 1950s, most White Baptists were content with a paternalistic approach of sponsoring ministry to Black Baptists, while keeping their schools, churches and social interaction segregated. There were some rare exceptions. Ken West recalls attending Gunnison Baptist Church, (Bolivar) in the 1950s, when the congregation had several Black members of the church, mostly women, who actively participated in WMU. However, most White Baptists agreed with W. Douglas Hudgins, pastor of First Baptist Church, Jackson (Hinds), who told reporters that he did not expect “Negroes” to try to join his church. When pressed specifically about the Brown v. Board of Education decision of the Supreme Court, Douglas evasively called it “a political question and not a religious question.” Alex McKeigney, a deacon from First Baptist Church, Jackson, was more direct, saying that “the facts of history make it plain that the development of civilization and of Christianity itself has rested in the hands of the white race” and that support of school desegregation “is a direct contribution to the efforts of those groups advocating intermarriage between the races.” Dr. D.M. Nelson, president of Mississippi College, wrote a tract in support of segregation that was published by the White Citizens’ Council in 1954. In the tract, Nelson said that in part, the purpose of integration was “to mongrelize the two dominant races of the South.” Baptist lay leader Owen Cooper recalled that during the 1950s, he avoided the moral issue that troubled him later: “To be quite honest I did not ask myself what Jesus Christ would have done had He been on earth at the time. I didn’t ask because I already knew the answer.”3
In 1960, Baptist home missionary Victor M. Kaneubbe sparked controversy over segregated schools for another racial group in Mississippi, the American Indians. Kaneubbe was a member of the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, who came to Mississippi to do mission work with the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians. However, since his wife was White, no public schools would admit their daughter, Vicki. The White schools denied Vicki because she was Choctaw, and the Choctaw schools denied her because she was White. Kaneubbe enlisted the support of many White Baptists who campaigned for Vicki. This eventually led to the establishment Choctaw Central High School on the Pearl River Reservation in Neshoba County, an integrated school that admitted students with partial Choctaw blood.4
The minutes of Woodville Heights Baptist Church, Jackson (Hinds) illustrate how local churches began to struggle with the issue of integration in the 1960s. At the monthly business meeting of Woodville Heights in August 1961, the issue of racial integration came up. The minutes read, “Bro. Magee gave a short talk on integration attempts. Bro. Sullivan gave his opinion on this subject. Bro. Sullivan said he would contact Sheriff Gilfoy concerning the furnishing of a Deputy during our services.” Interestingly, the very next month, the pastor, Dr. Percy F. Herring, resigned, and so did one of the trustees, Samuel Norris. In his resignation letter, Herring did not make a direct reference to the integration issue, only saying, “My personal circumstances and the situation here in the community have combined to bring me to the conclusion that I should submit my resignation as Pastor of this church.”5
Woodville Heights was not alone in the struggle. Throughout the 1960s, many Mississippi Baptists wrestled with racism in their local churches, associations, and the state convention. In the early part of the decade, it was common for Southern Baptist churches in Mississippi to have what was called a “closed door policy” against attendance by Black people. White Baptists were known to be active in the Ku Klux Klan, such as Sam Bowers, leader of the White Knights of the KKK, who taught a men’s Sunday school class at a Baptist church in Jones County. Some Baptist leaders were disturbed by the violence of the KKK. In November 1964, a few months after the murders of civil rights workers in Neshoba County, Owen Cooper presented a resolution on racism at the state convention. Cooper’s resolution, which was adopted, recognized that “serious racial problems now beset our state,” and said, “we deplore every action of violence… We would urge all Baptists in the state to refrain from participating in or approval of any such acts of lawlessness.” In 1965, it was front-page news in The Baptist Record when First Baptist Church, Richmond, Virginia admitted two Nigerian college students as members. When First Baptist Church, Montgomery, Alabama adopted an “open door policy” toward all races the same year, it was again news in The Baptist Record. Clearly, it was not yet the norm in White Mississippi Baptist churches.6
As the decade progressed, some Mississippi Baptists began to accept integration and work toward racial justice and reconciliation. Tom Landrum, a Baptist layman in Jones County, secretly spied on the White Knights of the Ku Klux Klan. Landrum’s reports to the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) were instrumental in the arrest of the Klansmen who killed civil rights leader Vernon Dahmer in 1965. Earl Kelly, in his presidential address in 1966, told the Mississippi Baptist Convention that “the race question” had to be faced. Baptist deacon Owen Cooper took this challenge seriously, helping to charter and becoming chairman of Mississippi Action for Progress (MAP) on September 13, 1966; MAP was able to secure millions of dollars to keep alive Head Start programs, which primarily benefitted impoverished Black children, that were in danger of losing their funds. When civil rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr. was assassinated in 1968, The Baptist Record quoted Baptist leaders who expressed “shock, grief and dismay at the murder” of King. In 1969, Jerry Clower, the popular Mississippi entertainer and member of First Baptist Church, Yazoo City (Yazoo), was speaking out against racism at Baptist events. Clower confessed that as a child, he was taught that “a Negro did not have a soul, but he found out he was wrong when he became a Christian.” By that year, 1969, all the state colleges and hospitals had agreed to sign an assurance of compliance with racial integration.7
(Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, to be published in 2025.)
SOURCES:
1 Jesse C. Fletcher, The Southern Baptist Convention: A Sesquicentennial History (Nashville: Broadman and Holman Publishers, 1994), 200; Annual, Southern Baptist Convention, 1954, 36; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1954, 45-49; The Baptist Record, June 10, 1954, 1, 3; July 8, 1954, 4.
3 Ibid, 62-63; Letter from Ken West, Leland, Mississippi, to Bob Rogers, Hattiesburg, Mississippi, 28 January 2022, Original in the hand of Robert C. Rogers; D. M. Nelson, Conflicting Views on Segregation (Greenwood, MS: Educational Fund of the Citizens’ Council, 1954), 5, 10; The Clarion-Ledger, April 4, 1982, cited in Dittmer, 63.
4 Jamie Henton, “Their Culture Against Them: The Assimilation of Native American Children Through Progressive Education, 1930-1960s,” Master’s Theses, University of Southern Mississippi, 2019, 85-92.
5 Minutes, Woodville Heights Baptist Church, Jackson, Mississippi, August 9, 1961; September 6, 1961.
6 Curtis Wilkie, When Evil Lived in Laurel: The ‘White Knights’ and the Murder of Vernon Dahmer (New York: W.W. North & Company, 2021), 26, 43-51; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1964, 43-44; The Baptist Record, January 28, 1965, 1; April 29, 1965, 2.
7 Wilkie, 20, 138; Dittmer, 377-378; The Baptist Record, November 17, 1966, 1, 3; December 21, 1967; April 11, 1968, 1; July 17, 1969, 1, 2; November 29, 1969, 1.
A challenge to Calvinism: M.T. Martin and the controversy that rocked Mississippi Baptists in the 1890s
Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
In 1893, a controversy began in the Mississippi Baptist Association and eventually spread across the state. Jesse Boyd wrote, “Its rise was gradual, its force cumulative, its aftermath bitter, and its resultant breach slow in healing.”1 While it may have been a quibble over words rather than a serious breach of Baptist doctrine, it illustrates how Mississippi Baptists clashed over Calvinist doctrine by the end of the 19th century.
M. Thomas Martin was professor of mathematics at Mississippi College from 1871-80, and he also served as the business manager of The Baptist Record from 1877-81. He moved to Texas in 1883, where he had great success as an evangelist for nearly a decade, reporting some 4,000 professions of faith. However, his methods of evangelism drew critics in Texas. According to J.H. Lane, while Martin was still in Texas, “the church in Waco, Texas, of which Dr. B. H. Carroll is pastor, tried Bro. Martin some years ago, and found him way out of line, for which he was deposed from the ministry.” In 1892 Martin returned to Mississippi and became pastor of Galilee Baptist Church, Gloster (Amite). Martin preached the annual sermon at the Mississippi association in 1893. His sermon had such an effect on those present, that the clerk entered in the minutes, “Immediately after the sermon, forty persons came forward and said that they had peace with God, and full assurance for the first time.” The following year, Mississippi association reported on Martin’s mission work in reviving four churches, during which he baptized 19 people, and another 60 in his own pastorate. Soon Mississippi Baptists echoed the Texas critics that he was “way out of line,” not because he baptized so many, but because so many were “rebaptisms.”2
The crux of the controversy was Martin’s emphasis on “full assurance,” which often led people who had previously professed faith and been baptized, to question their salvation and seek baptism again. In 1895, the Mississippi association called Martin’s teachings “heresy” and censured Martin and Galilee for practicing rebaptism “to an unlimited extent, unwarranted by Scriptures.” When the association met again in 1896, resolutions were presented against Galilee for not taking action against their pastor, but other representatives said they had no authority to meddle in matters of local church autonomy. As a compromise, the association passed a resolution requesting that The Baptist Record publish articles by Martin explaining his views, alongside articles by the association opposing those views, “that our denomination may be… enabled to judge whether his teachings be orthodox or not.” The editor of The Baptist Record honored the request, and Martin’s views appeared in the paper the following year. The association enlisted R.A. Venable to write against him, but Venable declined to do so. Martin also published a pamphlet entitled The Doctrinal Views of M.T. Martin. When these two publications appeared, what had been little more than a dust devil of controversy in one association, developed into a hurricane encompassing the entire state.3
Most of Martin’s teachings on salvation were common among Baptists. Even his opponent, J.H. Lane, admitted, “Some of Bro. Martin’s doctrine is sound.” Martin taught that the Holy Spirit causes people to be aware that they are lost, and the Spirit enables people to repent and believe in Christ. He taught that people are saved by grace alone, through faith, rather than works, and when people are saved, they should be baptized as an act of Christian obedience. Martin said that salvation does not depend on one’s feelings, and that children of God have no reason to question their assurance of salvation.
These teachings were not controversial. What was controversial, however, was what Lane called “doctrine that is not Baptist,” and what T.C. Schilling said “is not in accord with Baptists.” Martin said if a man doubted his Christian experience, then he was never true a believer.
He considered such doubt to be evidence that one’s spiritual experience was not genuine, and the person needed to be baptized again. “If you have trusted the Lord Jesus Christ,” Martin would say, “you will be the first one to know it, and the last one to give it up.” He frequently said, “We do wrong to comfort those who doubt their salvation, because we seek to comfort those whom the Lord has not comforted.” Therefore, Martin called for people who questioned their salvation to receive baptism regardless of whether they had been baptized before. “I believe in real believer’s baptism, and I do not believe that one is a believer until he has discarded all self-righteousness, and has looked to Christ as his only hope forever… I believe that every case of re-baptism should stand on its own merits, and be left with the pastor and the church.”4
The 1897 session of the Mississippi association took further action against Martinism. They withdrew fellowship from Zion Hill Baptist Church (Amite) for endorsing Martin and urged Baptists not “to recognize him as a Baptist minister.” The association urged churches under the influence of Martinism to return to the “old faith of Baptists,” and if not, they would forfeit membership. When the state convention met in 1897, some wanted to leave the issue alone, but others forced it. The convention voted to appoint a committee to report “upon the subject of ‘Martinism.’” Following their report, the convention adopted a resolution of censure by a vote of 101-16, saying, “Resolved, That this Convention does not endorse, but condemns, the doctrinal views of Prof. M. T. Martin.” While a strong majority condemned Martinism, a significant minority of Baptists in the state disagreed. From 1895 to 1900, the Mississippi association declined from 31 to 22 churches, and from 3,042 to 2,208 members. In 1905, the state convention adopted a resolution expressing regret for the censure of Martin in 1897.5
Earl Kelly observed two interesting doctrinal facts that the controversy over Martinism revealed about Mississippi Baptists during this period: “First, the Augustinian conception of grace was held by the majority of Mississippi Baptists; and second, Arminianism was beginning to make serious inroads into the previously Calvinistic theology of these Baptists.” It is significant that Mississippi association referred to Martinism as a rejection of “the old faith of Baptists,” and that when J.R. Sample defended Martin, Lane pointed out that Sample was formerly a Methodist.6
(Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, to be published in 2025.)
SOURCES:
1 Jesse L. Boyd, A Popular History of the Baptists of Mississippi (Jackson: The Baptist Press, 1930), 178-179.
2 Boyd, 196-197; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1893; 7; Z. T Leavell and T. J. Bailey, A Complete History of Mississippi Baptists from the Earliest Times, vol. 1 (Jackson: Mississippi Baptist Publishing Company, 1904), 68-69; The Baptist Record, May 6, 1897.
3 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1895; 1896, 9.
4 Boyd, 179-180; The Baptist Record, March 18, 1897, May 6, 1897, June 24, 1897, 2.
5 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1897, 6, 14; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1897, 13, 17, 18, 22, 31; 1905, 47-48; Leavell and Bailey, vol. 1, 70; Boyd, 198. Martin died of a heart attack while riding a train in Louisiana in 1898, and he was buried in Gloster.
6 Earnest Earl Kelly, “A History of the Mississippi Baptist Convention from Its Conception to 1900.” (Unpublished Doctoral Thesis, Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, Lousville, Kentucky, 1953), 114; The Baptist Record, May 6, 1897.
The Presbyterian spy in the Baptist Church

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
The first Baptist church in Mississippi not only faced persecution from the Catholic church but was infiltrated by a Presbyterian spy.
In the 1790s the Spanish controlled the Natchez District, outlawing all public worship that was not Roman Catholic. However, in 1791, Baptist preacher Richard Curtis, Jr. organized a church on Coles Creek, 20 miles north of Natchez, later known as Salem Baptist Church. The Spanish governor, Don Manuel Gayoso de Lemos, allowed private Protestant worship, hoping to win them over to Catholicism. However, when the priests in Natchez complained of the public worship of the Baptist congregation, Gayoso arrested Curtis in April 1795, and threatened to confiscate his property and expel him from the district if he didn’t stop. Curtis agreed, but he and his congregation decided that didn’t prohibit them from having prayer meetings and “exhortation.” Curtis even performed a wedding in May for his niece but did so secretly.
Sometime in 1795, Ebenezer Drayton was sent by Governor Gayoso to infiltrate the Baptist meetings and send back reports. He reported that at first the Baptists were “afraid of me, and they immediately guessed that I was employed by Government, which I denied.” However, he convinced them that his “feelings were much like theirs… my being of the Protestant Sect called Presbyterians and they of the Baptist.” Thus reassured, they allowed Drayton to attend their meetings, but Drayton wrote letters informing the Spanish “Catholic Majesty,” as he called him, of their activities.
Thanks to Drayton, the Spanish learned that Curtis started to go back to South Carolina, but the congregation sent four men to chase him down and insist he stay and preach to them. Considering this God’s will, Curtis returned and continued to preach. Drayton reported that Curtis agonized over his decision to stay, but told his congregation, “God says, fear not him that can kill the body only, but fear him that can cast the soul into everlasting fire… I am not ashamed not afraid to serve Jesus Christ… and if I suffer for serving him, I am willing to suffer… I would not have signed that paper if I had then known that it is the will of God that I should stay here.”
Drayton had a low opinion of Curtis and the Baptists. He wrote that the Baptists “are weak men of weak minds, and illiterate, and too ignorant to know how inconsistent they act and talk, and that they are only carried away with a frenzy or blind zeal about what they know not what…” However, Curtis seemed sharp enough to realize there was spy among them, because in July 1795, he published a letter in Natchez, explaining why he stayed, defending his religious freedom, and saying he was deeply hurt by “the malignant information against us, laid in before the authority by some who call themselves Christians.”
Thanks to their spy, the Spanish knew exactly when and where the congregation met. In August 1795, they sent a posse to arrest Curtis and two of his converts, but they fled to South Carolina, where they remained until the Spanish were forced by American authorities to leave the Natchez District.
Dr. Rogers is the author of a new history of Mississippi Baptists, to be published in 2025.
Two unique Baptists from Yazoo City, Mississippi: Owen Cooper and Jerry Clower


Article copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
Two of the most famous Baptists from Mississippi were laymen, not pastors. Both were members of the same church in Yazoo City, and one worked for the other.
Owen Cooper, an industrialist and deacon at First Baptist Church, Yazoo City, was a leader in Mississippi Baptist life for four decades, beginning in the 1940s. He founded Mississippi Chemical Corporation and led many humanitarian projects. Cooper eventually became the most influential layman in the Southern Baptist Convention in the twentieth century. He served as chairman of the board of trustees at New Orleans Baptist Theological Seminary at the time the seminary was relocated. He served on the Foreign Mission Board, where he worked closely with the area director for Southern Asia and the Pacific, Clinton native Jerry Rankin, on supporting indigenous missionaries in India. In 1959, he began serving on the Southern Baptist Executive Committee, a tenure that lasted 21 years. He was elected chairman of the SBC Executive Committee in 1971. In 1972, Cooper was elected president of the Southern Baptist Convention, serving two years. Other Mississippians had been elected president of the SBC, but they lived in other states at the time. Cooper was the first to live in Mississippi at the time he served as president of the SBC. An advocate for lay involvement in missions, Cooper was also the last layperson to be elected president of the denomination in the past 50 years. He died of cancer in 1986.
A native of Liberty, Jerry Clower was a fertilizer salesman who worked for Owen Cooper and a fellow church member of First Baptist, Yazoo City. When Clower released a record of his humorous stories, Cooper encouraged him, guaranteeing him a job if showbusiness didn’t work out. The record became a hit in 30 days, and the rest was history. In the 1970s, he began to appear regularly on “Country Crossroads,” a country and western show sponsored by the Southern Baptist Radio and TV Commission. In 1972, Clower nominated his boss and fellow church member Owen Cooper to be president of the Southern Baptist Convention with the memorable words, “Now y’all know he didn’t come to town on no watermelon truck.”2
SOURCES:
1 The Baptist Record, June 10, 1971, 1; June 22, 1972, 1; Don McGregor, The Thought Occurred to Me: A Book About Owen Cooper (Nashville: Fields Communications & Publishing, 1992), 94, 109, 127-128, 146, 149, 166-167, 169-170; “Owen Cooper (1908-1986) Business Leader and Humanitarian,” by Jo G. Prichard III, Mississippi History Now, accessed on the Internet March 7, 2023 at https://www.mshistorynow.mdah.ms.gov/issue/owen-cooper-1908-1986-business-leader-and-humanitarian;
2 The Baptist Record, September 14, 1972, 1; McGregor, 169.
(Dr. Rogers is writing a new history of Mississippi Baptists.)
How Mississippi Woman’s College became William Carey College
Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.

In the 1950s, the Mississippi Baptist Convention had to make a decision about what to do with Mississippi Woman’s College in Hattiesburg. Since reopening in 1947 under the leadership of Dr. Irving E. Rouse, the college enrollment grew steadily from 76 students to 149 by 1951. However, many felt that the all-female status of the college hindered its potential to grow. During debate over the issue, Sue Bell Johnson, wife of former president Johnson, prayed, “Lord, if Woman’s College can help bring in the Kingdom, save it.” In 1953, the Mississippi Baptist Education Commission presented the State Convention with two choices regarding the college: either close it, or make it co-educational. Messengers voted overwhelmingly to keep it open and make it co-educational. Then messengers took another vote on whether the college should be a junior college or a senior college, and by a vote of 304 to 291, they voted to make it a senior college. Knowing it could no longer be called “Woman’s College,” President Rouse suggested the name William Carey College, in honor of the 18th century English Baptist missionary to India who became the father of modern missions, and the new name was approved by the faculty and trustees. According to tradition, Rouse meditated in the forest adjacent to the college, and there felt inspired to name the school after the missionary. Thus, the college inherited the famous motto of William Carey, “Expect great things from God, attempt great things for God.”1
Even before Mississippi Woman’s College adopted its new name, the school began immediately to prepare for male students, erecting a male dormitory that opened in the fall of 1954. The administration knew that a quick way to bring in male students was by creating football, baseball, basketball and track teams. Les De Vall, head coach of Hinds Junior College in Raymond, was hired as the football coach. Billy Crosby, a member of the football and baseball teams, said that one day President Rouse asked if he would be interested in playing for Mississippi Woman’s College. Crosby thought, “I could just see the headlines: ‘The Skirts Lose Again.’” Nevertheless, Billy and 35 other players showed up that fall at the then-renamed William Carey College. With the addition of male students, the total enrollment in the fall of 1954 was 315 students. The football team posted winning seasons in its two years of competition, 1954 and 1955. An even greater spiritual victory occurred when Dr. Andy Tate, dean of men, led several of the football players to faith in Christ. These conversions sparked a revival in the men’s dormitory, and over 100 male students made professions of faith. Some of the athletes became ministers. The prayers of Sue Bell Johnson were already being answered.2
Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State (Mississippi Baptist Convention Board, 2025). The book is not sold in stores or on Amazon, but you may get a copy by making a donation ($15 suggested) to the Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission at this link, and tell them at the bottom of the form how many copies of the book you want: https://mbcb.org/historicalcommission/
SOURCES:
1 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1951, 114; 1953, 45; Donna Duck Wheeler, William Carey College: The First 100 Years (Charleston, SC: Arcadia Publishing, 2006), 43, 48, 49; The Baptist Record, May 13, 1954, 1; October 14, 2004, Special Supplement Celebrating the Jubilee of William Carey College.
2 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1954, 113; Wheeler, 51, 53.
How Mississippi Baptist churches struggled during the Great Depression

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
During the Great Depression, nearly every church had financial struggles, whether the church was large or small. First Baptist Church in Natchez had already begun a new building when the stock market crashed, dedicating their building in 1930. Unfortunately, the debt of approximately $25,000 proved a heavy burden during the depression, and it took them until 1945 to pay it off. The pastor, W. A. Sullivan, asked that his own salary be cut, and the difference be applied to the church debt. Despite this and other sacrifices, in January 1932 the church was unable to pay the interest on their loan. To avoid default, the church took out another loan to pay the interest on the first loan. It was not until 1939 that the financial situation improved enough that they began to pay down the principal on the debt; it took the Natchez church until 1945 to get out of debt1
First Baptist Church in Clinton borrowed money to build a new building in 1923, but struggled to pay the debt, as it was a small church, with a large majority of the members being college students with little income. The Clinton church’s building debt was a third of its income when the Great Depression came, and the church had little means to pay. In April 1933, the deacons recommended that the pastor serve a month without pay, and that payments to the debt be deferred for six months, paying only the interest. It would be another ten years before they finally paid the debt.2
Calvary Baptist Church in Jackson was a large congregation of 1600 members in 1930, but many members lost their jobs and left Jackson seeking work elsewhere. The hard times caused them to appoint a five-man committee to present a plan to cut expenses. At first, they proposed moderate cuts, eliminating salaries for choir members, getting rid of one telephone, and urging “strictest economy” in electricity and water use. But as offerings continued to fall, they slashed other salaries and stopped purchasing Sunday school literature.3
When the Great Depression started, C. J. Olander was pastor of several churches in the Rankin County area, including First Baptist of Brandon, Bethel, Fannin and Pisgah churches, and he started the church at Flowood. Olander wrote later, “The depression became so severe that the members [at Flowood] moved out for the time being and came back and reorganized.” The Brandon Church paid him $450 a year. To supplement his income, Olander sold milk to townspeople and kept a good garden for food. In 1935, Olander went to the Delta to pastor five churches at once, even though a friend warned him that if he went there, “you will never be heard of again and the folk will starve you to death.” Olander said, “It was bad, it was bankrupt, yet today as a result of that ministry there are six full time churches. There was Morgan City, Tchula, Blaine, Cruger, Sidon and Harmony.”4
Some churches managed to thrive despite the Depression. A. L. Goodrich was called to pastor First Baptist Church, Pontotoc, just 30 days before the banks closed. Rather than let it dampen his spirits, Goodrich focused on sharing the gospel and helping his community. The energetic pastor joined local civic clubs, he took leadership positions in his Association and the State Convention, and he organized the “Pontotoc Cotton Plan” to give hundreds of dollars to the Mississippi Baptist Orphanage. God blessed the church with an increase of 232 members during his years as pastor, 1931-1935. The Pontotoc church’s Sunday night worship attendance was equal to morning worship; they started three choirs, paid off an old debt and installed a pipe organ.5
Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State (Mississippi Baptist Convention Board, 2025). The book is not sold in stores or on Amazon, but a copy can be obtained by making a donation ($15 suggested) to the Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission at this site: https://mbcb.org/historicalcommission/ .
SOURCES:
1 “A History of First Baptist Church, Natchez, Mississippi, 1817-2000,” Unpublished document, Archives, Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission, 17-19; Daniel A. Wynn, “History of First Baptist Church of Natchez,” in Forward to Freedom: The 175th Anniversary Celebration, First Baptist Church, Natchez, Mississippi, April 26, 1992.
2 Charles E. Martin, A Heritage to Cherish: A History of First Baptist Church, Clinton, Mississippi, 1852-2002 (Nashville: Fields Publishing, Inc., 2001), 93-96.
3 Randy J. Sparks, Religion in Mississippi (Jackson: University Press of Mississippi, 2001), 183.
4 Tom J. Nettles, The Patience of Providence: A History of First Baptist Church Brandon, Mississippi, 1835-1985 (First Baptist Church, Brandon, Mississippi, 1989), 69, 72-73.
5 The Baptist Record, January 3, 1935, 5.
The story of Dan Moulder, perhaps Mississippi’s greatest country preacher

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
One of the greatest country preachers in the history of Mississippi was the remarkable Daniel Wesley Moulder of Lorena in Smith County. He served as pastor of as many as 11 churches at once. Born on November 26, 1867, Moulder was in his 60s at the time of the Great Depression, yet “Brother Dan” was still going strong. He preached at different locations every weekend, multiple times every Saturday and Sunday, and even occasionally on Friday night. Moulder eventually served 42 different churches in Smith, Simpson, Jones, Rankin, Hinds, Covington and Scott Counties, 16 of which he organized. In 1932, he preached 330 sermons in churches of which he was pastor, and 40 more sermons in other churches. He baptized 117 people in 1932, received 75 other new members, conducted 70 funerals, and performed six weddings. In 1933, Moulder was already serving 10 different churches at once as pastor when he organized another at Lorena in Smith County. During the Great Depression, each weekend he preached to churches scattered across Simpson, Smith and Rankin Counties. He once told a preacher who said he had nothing to preach, “Get your Bible and go among your people. You’ll receive more than you’ll ever be able to preach.” When he died in 1953, he was buried at Goodwater Baptist Church in Smith County, the church where he had been ordained. The Mississippi Baptist Convention annual honored Moulder as “one of Mississippi’s greatest country preachers,” and the Smith County Baptist Association remembered him as “Mississippi’s most widely known and best-loved minister.”
Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, (Mississippi Baptist Convention Board, 2025). The book is not sold in stores or on Amazon, but it can be obtained from the Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission by making a donation (suggested $15) at this link: https://mbcb.org/historicalcommission/
SOURCES: The Baptist Record, March 17, 1932; January 5, 1933, 1, 5; December 13, 1990, 2; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1953, cover page; Minutes, Smith County Baptist Association, 1953; Letter, D. W. Moulder to J. L. Boyd, January 14, 1927, Archives, Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission.
The Mississippi Delta preacher and his train ticket

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
Mississippi Baptists are primarily a rural people, and during the Great Depression, many of these churches could only afford to pay their pastors with vegetables, chickens, eggs and meat from their gardens and farms. The only way that many small country churches could find a pastor was to have one come once or twice a month, and share him with other churches. In 1930, Will Turner, a leader from Straight Bayou Baptist Church in Sharkey County talked to C. C. Carraway, the young pastor of Midnight Baptist Church. Turner asked Carraway if he would preach at Straight Bayou, as well. Carraway, who was a student at Mississippi College, said he would. Turner asked how much his round-trip train ticket cost from Clinton to Midnight, and he said it was $4.28. Turner said, “Then that’s what we’ll pay you each time you come.”
Source: “Straight Bayou Baptist Church: The First Hundred Years, 1891-1991,” Straight Bayou Baptist Church, Anguilla, Miss., Unpublished document, Archives, Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission, 12.
Arthur Flake, the man from Mississippi who changed the face of Sunday School

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
Arthur Flake was born in Texas, but moved to Winona, Mississippi in 1895 when he married Lena Nelson. A traveling salesman and department store manager, Flake was a gifted organizer who changed the face of Sunday School in the Southern Baptist Convention. In 1895 he organized the first Baptist Young People’s Union (B.Y.P.U.) in Mississippi in his church in Winona. He also served as a volunteer Sunday School superintendent in his church, and he was so successful that he was elected in 1909 as a field worker with the Sunday School Board of the Southern Baptist Convention. In 1920, he was placed in charge of standardizing how Southern Baptists do Sunday School. He developed his famous “Flake’s Formula” for growing a Sunday School: discover the possibilities, enlarge the organization, provide a place, train the workers, and visit the prospects. Baptist historians point to God’s work through Arthur Flake as a major reason that Southern Baptists have had more growth through Sunday School than other denominations.
SOURCES:
“Flake, Arthur,” in Encyclopedia of Southern Baptists, vol. 1, (Nashville: Broadman Press, 1954), 440-441; Jesse C. Fletcher, The Southern Baptist Convention: A Sesquicentennial History (Nashville: Broadman & Holman Publishers, 1994), 123.
The beginnings of William Carey University

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
Since Mississippi College was an all-male school, Mississippi Baptists were looking to sponsor a college for women in the early twentieth century, and the opportunity fell into their lap in Hattiesburg.1
A group of New Orleans businessmen had founded South Mississippi College in Poplarville in 1906, and then immediately moved it to land in the south part of Hattiesburg. Under the leadership of William I. Thames, it quickly grew, but then tragedy struck. On the night of February 28, 1910, a devastating fire destroyed the main building, eliminating classrooms, the library, and the auditorium. The school was forced to close. In 1911, W. S. F. Tatum, a wealthy lumberman and Methodist layman, bought the 10 acres and remaining two buildings. Tatum offered the property to the State of Mississippi for a “Normal College” (teacher’s college), but the site was rejected by the State. He then offered the property to his fellow Methodists, but they chose not to build another college, since they already had Millsaps College in Jackson. He then offered it to as a gift to the four Baptist churches in Hattiesburg. Those churches accepted the offer, formed a corporation, and the trustees hired W. W. Rivers from Arkansas to become president. Rivers secured a faculty, recruited students, and opened the school in September 1911 under a new name, Mississippi Woman’s College. They offered the debt-free college to the Mississippi Baptist Convention, and it was accepted by the State Convention on November 23, 1911.2
John L. Johnson, Jr. served as president of Mississippi Woman’s College from 1912-1921, and during his administration an administration building, Tatum Court, was completed in 1914, and brick dormitories, Ross and Johnson Halls, were added, as well as an infirmary and a model home to be used as a laboratory for domestic science classes. Enjoying rapid growth in enrollment, the campus expanded to 40 acres, and gained accreditation by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools in 1926. By 1929, the college had 500 students. This school later became William Carey University, which will be the subject of a future blog post.3
Dr. Rogers is currently writing a new history of Mississippi Baptists.
SOURCES:
1 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1900, 63.
2 Donna Duck Wheeler, William Carey College: The First 100 Years (Charleston, SC: Arcadia Publishing, 2006), 8, 16-17; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1911, 55-56.
3 Wheeler, 8; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1919, 22-23; 1929, 55.
The racial segregation in Mississippi Baptist churches after the Civil War

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
One the most significant social changes among Mississippi Baptists after the Civil War was the racial segregation of churches. Before the war, African people who were enslaved constituted a substantial portion of Mississippi Baptist congregations, as I have discussed in previous blog posts. In the decade after the war, Black Baptists gradually celebrated their new freedom by separating into independent, self-governing churches. In some areas this happened suddenly, and in other areas of the state it was more gradual. The First Baptist Church of Clinton, for example, had a membership of 283 in 1860, including 113 Black members. In 1866, with the absence of college students and withdrawal of Black members, the Clinton church was reduced to 36 members, and worship was only held once a month, led by a pastor from Raymond. In 1864, Jerusalem Baptist Church had 65 Black members, but all of them were gone by 1866. Bethesda Church in Hinds County agreed in 1867 to allow Black members to hold a separate revival meeting, and later in the same year the church granted the following request: “The colored members signified a desire to withdraw from the church to organize an independent church and asked permission for the use of the church house one sabbath each month.” Likewise, Black members of Academy Baptist Church in Tippah County met separately after the war, and had a Black preacher, but used the Academy church building until the 1870s. Charles Moore, a preacher who had been enslaved, expressed the common desire of Black Baptists after the war, “I didn’t expect nothing out of freedom excepting peace and happiness and the right to go my way as I please. And that is the way the Almighty wants it.”1
In other areas, Black members continued to worship alongside Whites in the same churches for a decade or more. Ebenezer Baptist Church in Amite County continued to refer to “colored” members frequently through 1874, and then there was one more mention in 1877 of a “colored” member who asked to be restored so that he could join New Hope Baptist Church. Although most churches remained integrated for several years, tensions began to arise, sometimes fueled by resentment over events of the war. For instance, in September 1865, five months after the war ended, “Eliza a colored woman” joined Sarepta Baptist Church in Franklin County by her experience of faith, and “it was moved and seconded that the right hand of fellowship be extended which was done with the exception of one brother who refused to give the right hand of fellowship to the colored woman Eliza.”2
Despite this occasional White resentment, most White Baptist leaders expressed goodwill to Black Baptists. In 1870, Salem Baptist Association in Jasper County recommended that if Black members “wish to form churches of their own, that they should be dismissed in order and assisted in doing so, but where they wish to remain with us as heretofore and are orderly, we think they should be allowed to do so.” Black membership in Salem Association declined from 206 in 1865 to 122 in 1870. As late as 1872, 81 Black people continued to worship in biracial churches in the association, and Black people continued in the records of Fellowship Baptist Church as late as 1876. The Mississippi Baptist Association reported 131 Black members in 1874.3
Segregation of Mississippi Baptist churches started out as a celebration of freedom for Black people, but by the 1890s, it had also become an expectation of Whites. The Mississippi Baptist Convention assumed that their churches were made up of White members only. For instance, the 1890 state convention referred to itself as: “The Mississippi Baptist Convention… representing a denomination of 80,000 white Christians…” However, the state convention maintained friendly relations with “colored” Baptists, a term considered polite at the time. When the General Baptist Convention of Mississippi, made up of African Americans, met at the same time as the Mississippi Baptist Convention, they frequently exchanged telegrams of Christian greetings. Mississippi Baptist pastors frequently led Bible institutes for Black Baptist pastors and deacons, and the state convention encouraged White pastors to donate their time to teach at these institutes across the state.4
SOURCES:
1 Charles E. Martin, A Heritage to Cherish: A History of First Baptist Church, Clinton, Mississippi, 1852-2002 (Nashville: Fields Publishing, Inc., 2001), 36; Randy J. Sparks, Religion in Mississippi (Jackson: University Press of Mississippi, 2001), 139.
2 Minutes, Ebenezer Church, Amite County. November 1, 1873, May 2, 1874, October 3, 1874, July 1, 1877; Minutes, Sarepta Church, Franklin County, September 1865.
3 Sparks, 139-140; Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Association, 1874.
4 Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1890, 31; 1891, 14; 1897, 20-21.
Dr. Rogers is the author of Mississippi Baptists: A History of Southern Baptists in the Magnolia State, which was published in 2025. You can get a copy of his book by making a donation to the Mississippi Baptist Historical Commission at the following link and telling them how many copies of the book you wish: https://mbcb.org/historicalcommission/ (Suggested donation $15).
The first Baptist missionary to the Mississippi Gulf Coast, John B. Hamberlin

Copyright by Robert C. Rogers and the Mississippi Baptist Convention Board.
Although Baptists were well-established in the rest of Mississippi, they were late getting started on the Mississippi Gulf Coast. In 1868, the Mississippi Baptist Convention listed the names of the Baptist ministers in Mississippi and their post offices, nearly all of which were in north or central Mississippi. Not a single Baptist minister resided on the Mississippi Coast. In 1873, W. H. Hardy of Meridian called attention to the lack of Baptist churches in Jones, Perry, Greene, Harrison and Hancock counties, and “the populous towns along the sea shore.” He called for the Convention to send missionaries to Pascagoula or Pass Christian “or some other convenient point.”
In 1875, the Mississippi Baptist Convention sent John B. Hamberlin as a missionary to the Mississippi Coast, where, he reported, there was “only one little Baptist church, and that in a disorganized state.” This church was located three miles in the country from Ocean Springs, and he relocated it in the town. He also started a church in Moss Point, which built a house of worship. Next, he targeted Biloxi, where “Roman Catholicism overshadows everything.” He found “a poor old widow” who was the only member left of a small Baptist congregation that once had a house of worship there. “He got possession of the old house, made some repairs upon it; has conducted two special meetings, and has recently organized a church of seventeen members.” Sadly, a yellow fever epidemic in 1876 took the life of Hamberlin’s wife while they were in Biloxi, and he sent his small child inland to get away from the epidemic, while he returned to his mission work on the Coast. Hamberlin wrote, “My wife is dead; my home is broken up; my child is gone, and my heart is desolate; but I hope in the future to be a better man, and to do more and better work for Christ than ever before.”
SOURCE:
Minutes, Mississippi Baptist Convention, 1868, 22-23, 29-30; 1873, 17-18; 1875, 12; 1876, 24-25.

